Our Science
We are a clinical-stage pharmaceutical company with a rich pipeline of precision-targeted neuroscience programs designed to improve the lives of patients with neuropsychiatric and neurodevelopmental diseases. At Engrail, we apply precision chemistry and pharmacology to develop transformative medicines for patients who have been underserved by existing treatments. This approach has facilitated the development of targeted drugs with optimized profiles and high probability of success.
GABA MODULATION
GABA is the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain.1 Enhancing inhibitory neurotransmission is a proven therapeutic approach for the treatment of anxiety, pain, and a broad array of other indications.2-4
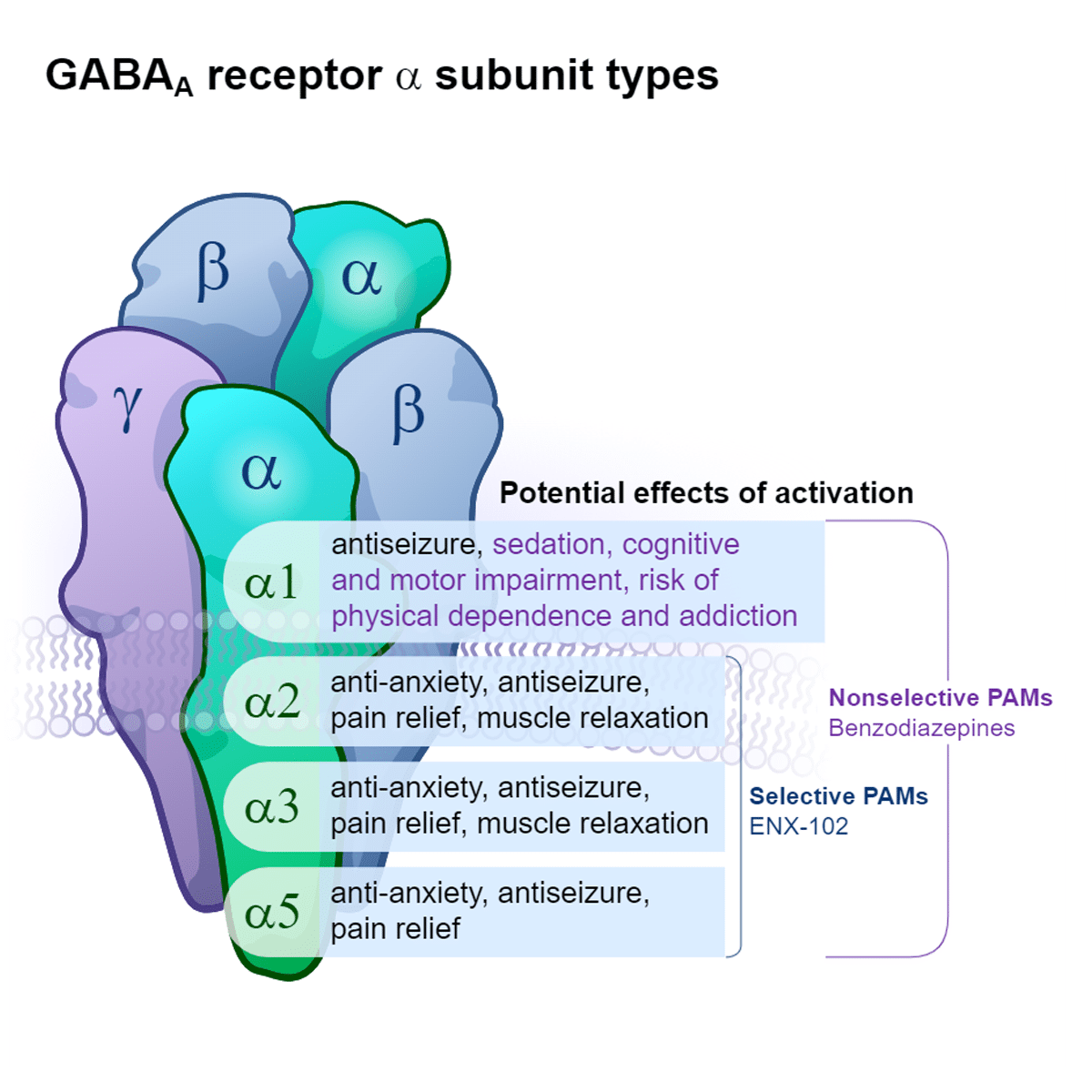
Benzodiazepines are the most widely known GABA modulators and provide remarkable efficacy for short-term use, but their chronic use is often limited by loss of efficacy over time as well as significant side effects (e.g., sedation, cognitive impairment, motor impairment) and risks (e.g., physical dependence, addiction potential). Benzodiazepines are conventional, nonselective GABAA positive allosteric modulators (PAMs) that drive function at GABAA receptors containing α1, α2, α3, or α5 subunits.5,6 Whereas activity at all α subunits can contribute to the efficacy of benzodiazepines, specific activity at α1 is thought to drive many undesirable side effects and risks.5-7
Our scientific expertise in GABAA receptor pharmacology and neurocircuitry has led to the development of precision-targeted therapies that maximize the clinical benefits of GABA modulation while minimizing the undesirable side effects and risks associated with benzodiazepines.

- Enhanced and sustained efficacy with chronic use
- Improved tolerability
- Ease of administration

Dopamine Modulation
Dysregulated dopamine neurotransmission, particularly in brain reward circuitry, plays a role in depression and other mood disorders.1,2
A hallmark symptom of major depressive disorder is anhedonia, which is the loss of ability to feel pleasure. There are no treatments for depression that target this core symptom, and anhedonia is associated with a poor response to currently available antidepressant treatments.1
A selective therapy that increases dopamine neurotransmission has the potential to improve the symptoms of depression, including anhedonia — a significant unmet need in the treatment of depression.1
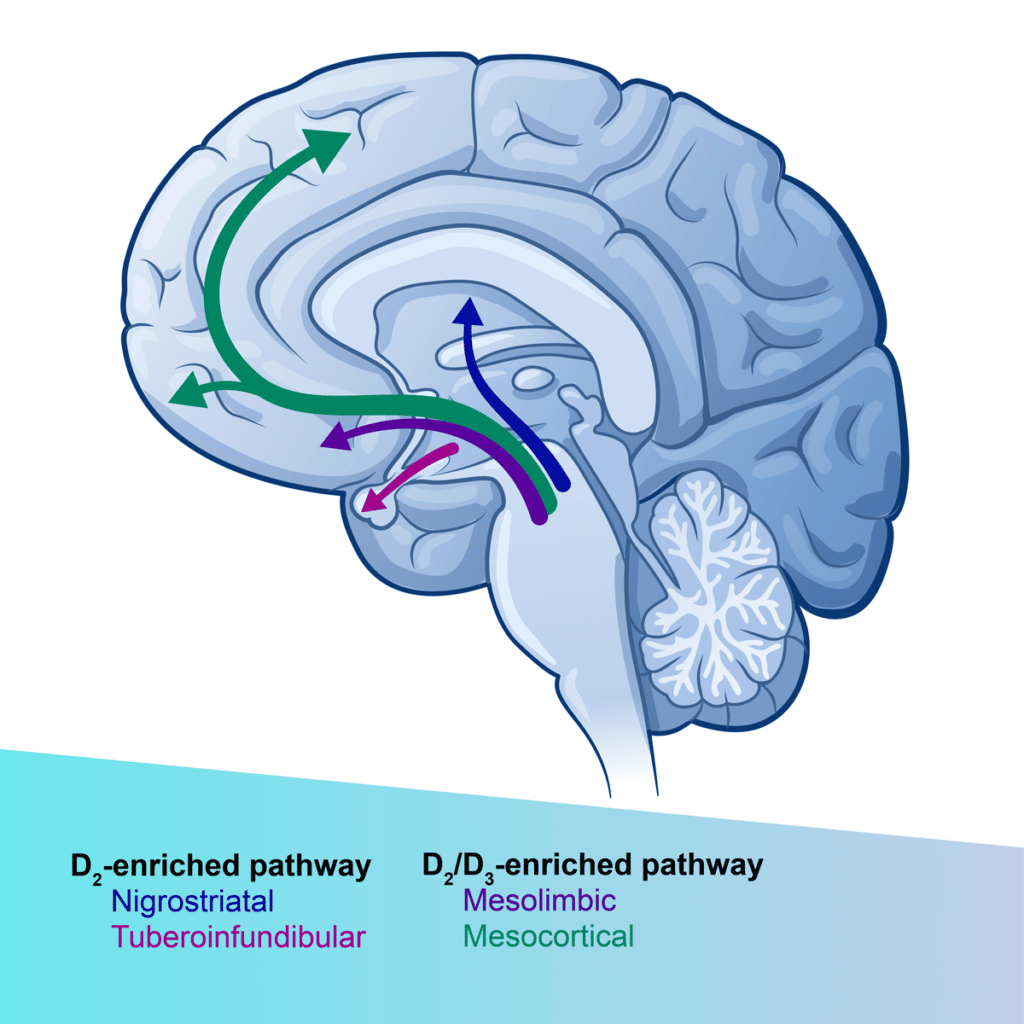
The role of dopamine D2/D3 receptors in regulating mood and reward processing is well established.3 At low doses, D2/D3 receptor antagonists preferentially block presynaptic autoreceptors to increase dopamine release.4 Our compound ENX-104 is a highly potent and selective D2/D3 receptor antagonist with excellent brain pharmacokinetics. It is well-positioned to provide an anti-anhedonic therapeutic response at low doses, with a favorable safety and tolerability profile.5
Neurotransmission of both serotonin and dopamine have important central regulatory effects and can modulate one another.2,6-8 In addition to the role of dopamine in regulating reward processing, serotonin plays a key role in emotion processing.3,9 ENX-205 is a 5-HT1A/5-HT2A receptor agonist and D2/D3 receptor antagonist. This unique pharmacology may drive therapeutic benefits for the treatment of posttraumatic stress disorder as well as a wide variety of mood disorders.5
COPPER TRANSPORT
Copper plays a central role in many cellular processes throughout the body; however, its levels need to be tightly regulated to prevent deficiency and excess, which are both damaging to cells.1
The major regulator of copper levels in cells is ATPase copper transporting alpha (ATP7A), a transmembrane protein that shuttles copper from the gut into various organs, including the brain.1,2 Loss-of-function mutations in ATP7A impede copper distribution and result in Menkes disease.2 This fatal, ultra-orphan disease is characterized by a severe lack of copper in the brain and a toxic excess of copper in other tissues, such as the kidneys.2-4
A therapy that can enable proper copper distribution without relying on ATP7A may have the potential to increase survival and improve quality of life for patients with Menkes disease.
ENX-203 is a copper ionophore designed to address the underlying copper transport defect in Menkes disease.5 This unique mechanism of action allows copper to be transported into the brain, where it is essential for cellular respiration and energy production contributing to brain health and growth.
+ References and Abbreviations
GABA modulation:
GABA, gamma-aminobutyric acid; PAM, positive allosteric modulator.
1. Wu C & Sun D. Metab Brain Dis. 2015;30:367–379. 2. Bialer M, et al. Epilepsia 2020;61:2365–2385. 3. Wright SL. Adv Ther. 2020;37:2604–2619. 4. DeMartini J, et al. Ann Intern Med. 2019;170:ITC49 –ITC64. 5. Vinkers CH & Olivier B. Adv Pharmacol Sci. 2012;2012:416864. 6. Castellano D, et al. Front Neurosci. 2021;14:616298. 7. Licata SC & Rowlett JK. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2008;90:74–89. 8. Engrail Therapeutics. Data on file.
Dopamine modulation:
D2, dopamine receptor 2; D3, dopamine receptor 3.
1. Belujon P & Grace AA. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017;20:1036–1046. 2. Grace AA. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2016;17:524–532. 3. Stahl SM. CNS Spectr. 2017;22:375–384. 4. Schoemaker H, et al. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997;280:83–97. 5. Engrail Therapeutics. Data on file. 6. Ressler KJ & Nemeroff CB. Depress Anxiety. 2000;12(Suppl. 1):2–19. 7. Daw ND, et al. Neural Netw. 2002;15:603–616. 8. Wong PT, et al. Neurosci Res. 1995;23:115–119. 9. Lucki I. Biol Psychiatry. 1998;44:151–162.
Copper Transport:
1. Kaler SG. ATP7A-related copper transport diseases-emerging concepts and future trends. Nat Rev Neurol. 2011;7(1):15–29. 2. Bhattacharjee A et al. The Activity of Menkes Disease Protein ATP7A Is Essential for Redox Balance in Mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 2016; 291 (32):16644–16658. 3. Horn N, Wittung-Stafshede P. ATP7A-Regulated Enzyme Metalation and Trafficking in the Menkes Disease Puzzle. Biomedicines. 2021;9(31):1–38. 4. Ramani PK, Parayil Sankaran B. Menkes Kinky Hair Disease. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. 2022. Accessed 30.01.2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560917/. 5. Guthrie LM et al. Elesclomol alleviates Menkes pathology and mortality by escorting Cu to cuproenzymes in mice. Science. 2020;368(6491):620–625